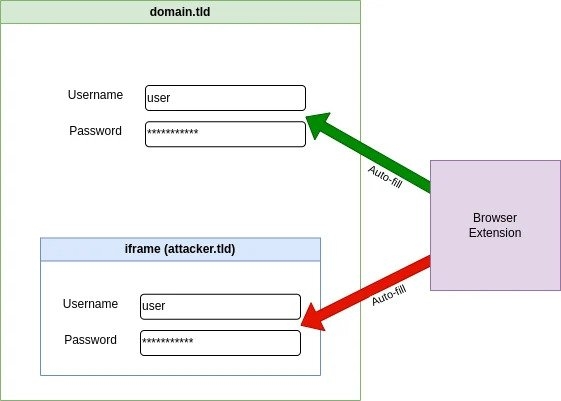
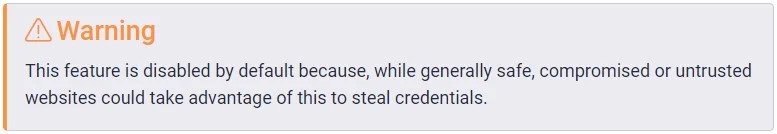
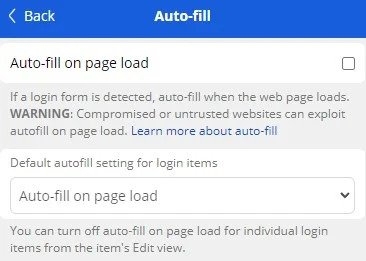
Moving on, the Bitwarden autofill feature holds a dangerous behavior that could allow malicious iframe planted in trusted websites to steal users’ credentials and send them to the attacker. As per the security firm, Bitwarden learned about the issue in 2018, but it still chooses to allow it to be with trusted websites that use an iframe. With that being said, though, the autofill feature is not active by default, and the state of utilizing it arent much. However, some websites meet the requirement, and any prompt threat actor will try to exploit these flaws. Well, a user visits a website, the extension of the password manager scans if there’s a stored login for the domain and offers to fill in the credentials, and if the autofill is turned on, it fills it automatically as the page loads without the user having to do anything. Now, after analyzing Bitwarden, the security firm’s analyst found out that the extension also autofill forms specified in the embedded iframe, even those from the exterior domain. Although the iframe does not have access to the content on the main page, it waits for the login form and then forwards the credentials added by the user to a remote server without any further user interactions, says Flashpoint. Read: Threat Actors Exploit OpenAI’s ChatGPT Popularity to Distribute Malware Furthermore, Flashpoint investigated how often the iframe is planted on the login page of websites with high traffic and said that the amount of risky cases is low, notably lowering the risks. However, there’s still a second issue that the security firm found while it was investigating the iframe issue. Well, the password management service also autofill the credentials on the sub-websites of the main website matching the login. This indicates that if the attacker has hosted a phishing page under the subdomain that matches the stored domain login of the base domain, it will steal the credentials of the user visiting the website if the autofill feature is turned on. In a report, Flashpoints mentions that some content hosting allows hosting arbitrary content under a subdomain of their official domain, which also serves as the login page. For instance, an enterprise has a login page at http: //login.company.tld and lets users serve content under https:// <clientname<company.tld; these users were able to steal the credentials from Bitwarden extension Well, after all this, Bitwiden has acknowledged that the autofill feature is a potential risk and also includes a warning in its declaration, particularly mentioning the possibility of infected sites exploiting the autofill feature to steal credentials. Although the flaw has been brought to light in a security assessment that was done on November 2018, the company is already aware of the issue for some time now. Since the user needs to log in to the service using the planted iframe from an external domain, the devs at Bitwarden decided to keep this unchanged and add a warning on the software’s declaration and the extension applicable settings. Answering the security firm’s second report about URL handling and how the autofill controls the subdomain, the company assured to block autofill on the reported hosting in an update but does not plan on changing the iframe functionality. Read: BidenCash Leak: 2M+ Credit/Debit Cards with Personal Info Exposed